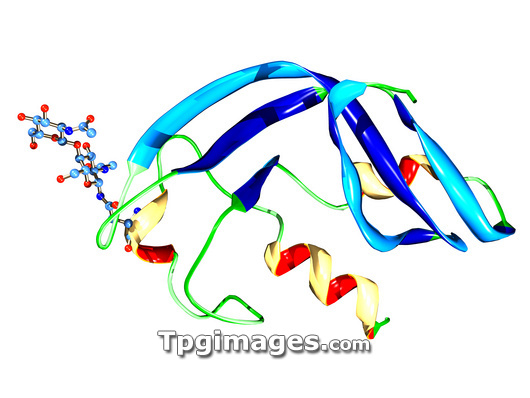
Synthetic ribonuclease molecule. Molecular model showing the secondary structure of amphinase, a synthetic version of a ribonuclease molecule found in the egg cells of the northern leopold frog (Rana pipiens). Ribonucleases are enzymes that break up RNA (ribonucleic acid), a molecule used to translate genes into their protein products. Amphinase attaches to glycoproteins on a cell, before invading the cell and killing it by destroying its RNA. Here the amphinase molecule is attached to NAG (N-acetyl-D-Glucosamine, ball and stick structure) a human glycoprotein. Amphinase could potentially be used as an anti-tumour drug, as tumours (especially brain tumours) are covered in glycoproteins (unlike healthy cells).
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP03197742
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading