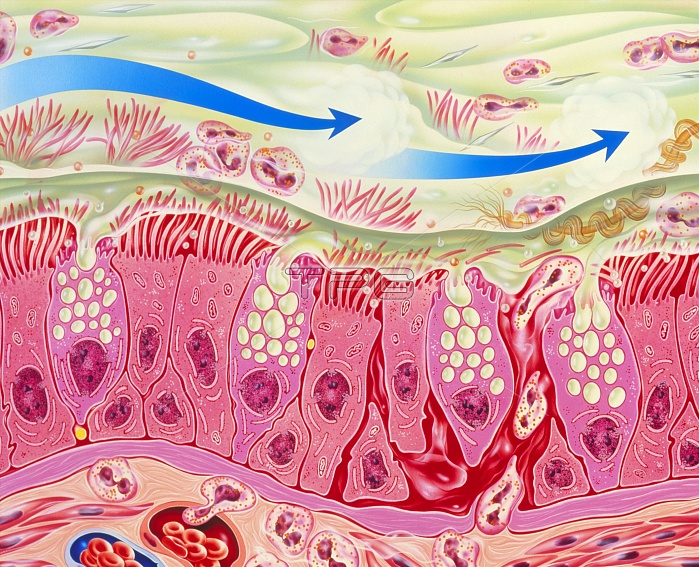
Bronchial inflammation in asthma. Artwork of bron- chial epithelial tissue inflamed by asthma. A thick layer of mucus (green) covers the tissue. This is produced by goblet cells interspersed among ciliated epithelial cells. The connective tissue at the bottom contains enlarged blood vess- els (lower left) and numerous eosinophil white blood cells, which are also abundant in the mucus. Eosinophils play a major role in allergic inflam- mations. They secrete chemicals that are partly responsible for the bronchial constriction that occurs in asthma. Epithelial desquamation (shed- ding of outer layer of cells) is shown at right. The blue arrows symbolise drugs taken by inhaler.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP10195412
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading