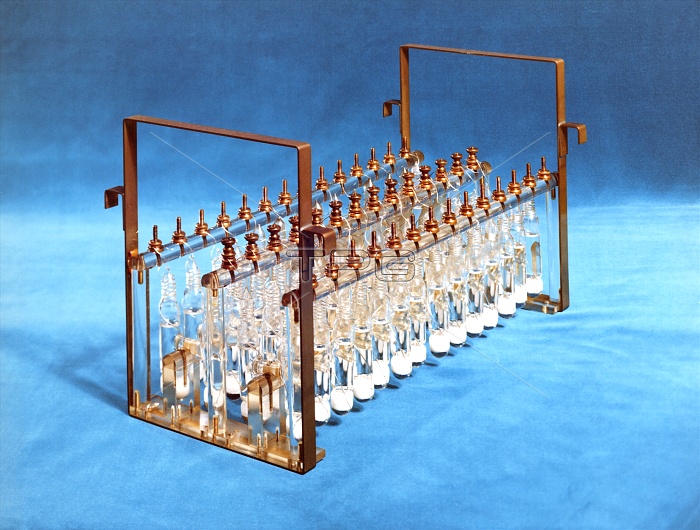
Bank of Weston cells. These electrochemical cells produce a stable voltage used as a standard to calibrate voltmeters and define the SI unit for electromotive force (the volt). Also called a standard cell, it were invented in the USA by physicist Edward Weston in 1893. They have cadmium-mercury anodes (top of glass tube), with cathodes of liquid mercury (bottom of tubes) covered by mercury sulphate (white) and mercury. The electrolyte is a clear solution of cadmium sulphate. Weston cells provided the standard for voltage measurements between 1911 and 1990. Photographed at the National Physical Laboratory, Teddington, UK.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP10710598
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
No
Property Release:
No
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading