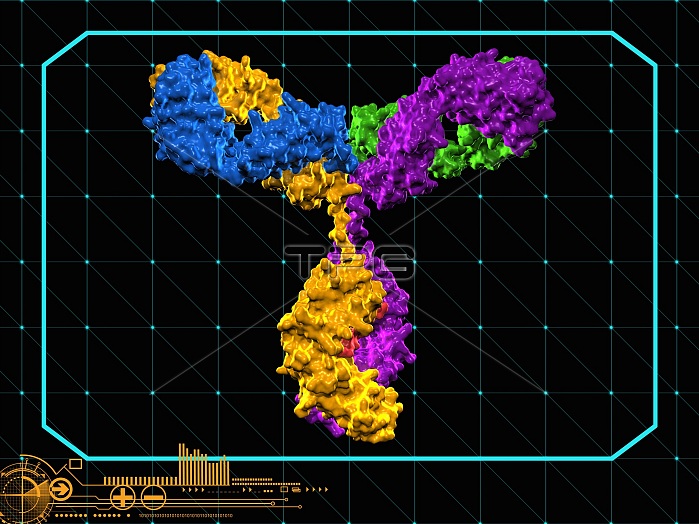
Immunoglobulin G antibody molecule. Computer model of the secondary structure of immunoglobulin G (IgG). This is the most abundant immunoglobulin and is found in all body fluids. Each Y-shaped molecule has two arms (top) that can bind to specific antigens, for instance bacterial or viral proteins. In doing this they mark the antigen for destruction by phagocytes, white blood cells that ingest and destroy foreign bodies. Antibodies can also kill some pathogens directly, and can neutralise toxins.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP19950778
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading