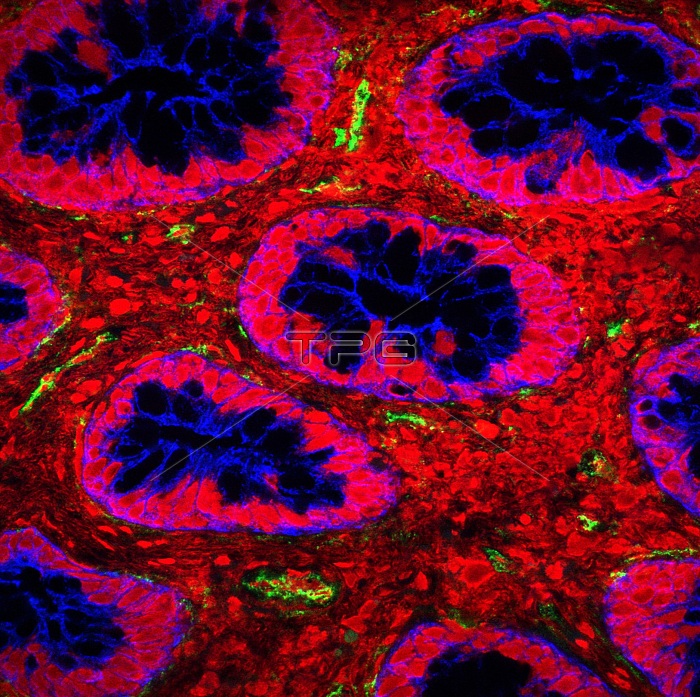
Bacterial toxin in the intestine of a child. Intestinal biopsy from a child infected with shiga toxin-producing E. coli. Shiga toxin (Stx) is an extremely potent toxin and is produced when the bacterium contains a bacteriophage carrying the toxin gene. It is closely linked with Haemolytic Uremic Syndrome and acute renal failure in children. After ingestion via contaminated food or water the E. coli bacteria colonize the gut and produce the toxin, which then crosses the gastrointestinal barrier to enter the systemic circulation and reach the kidney and other target organs. In this image, the toxin (green) has crossed into the intestine and is binding to the endothelial cells of the lamina propria (red). Confocal micrograph.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP22239480
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
No
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading