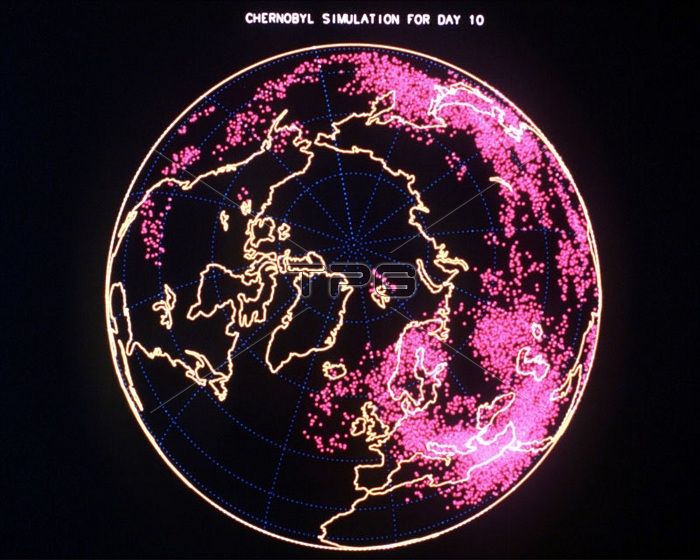
ARAC simulation showing the dispersion of radioactivity after the Chernobyl accident in 1986. The Chernobyl disaster was a catastrophic nuclear accident that occurred on April 26, 1986 at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in Ukraine (then officially the Ukrainian SSR). An explosion and fire released large quantities of radioactive particles into the atmosphere, which spread over much of the western USSR and Europe. The Chernobyl disaster is the worst nuclear power plant accident in history in terms of cost and casualties, and is one of only two classified as a level 7 event (the maximum classification) on the International Nuclear Event Scale. The Atmospheric Release Advisory Capability (ARAC) at Lawrence Liverrnore National Laboratory is a centralized federal project for assessing atmospheric releases of hazardous materials in real time. Since ARAC began making assessments in 1974, the project has responded to over 60 domestic and international incidents. Although it was originally conceived and developed as an emergency response and assessment service for providing dose-assessment calculations after nuclear accidents, it has proven to be an extremely adaptable system, capable of being modified to respond also to non-radiological hazardous releases.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP22301046
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
No
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading