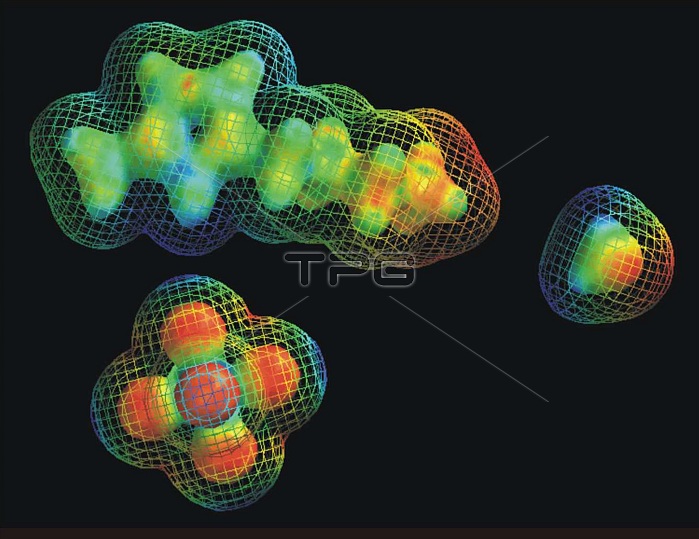
Molecular "space filling" models demonstrate the difference in size for the positively charged "cation" (top image) and the negatively charged "anion" (bottom left) that combine to form a promising ionic liquid. It is still a mystery how the much smaller water molecule (right) can have such a large effect on the viscosity of such ionic liquids. People in industry are very interested in using ionic liquids because unlike most organic solvents, they don't evaporate and they are not flammable. A cation is an ion with fewer electrons than protons, giving it a positive charge. An anion is an ion with more electrons than protons, giving it a net negative charge. An ionic liquid (IL) is a salt in the liquid state. While ordinary liquids such as water and gasoline are predominantly made of electrically neutral molecules, ionic liquids are largely made of ions and short-lived ion pairs. These substances are variously called liquid electrolytes, ionic melts, ionic fluids, fused salts, liquid salts, or ionic glasses. Ionic liquids have many applications, such as powerful solvents and electrically conducting fluids (electrolytes). Salts that are liquid at near-ambient temperature are important for electric battery applications, and have been used as sealants due to their very low vapor pressure.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP22302088
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
No
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading