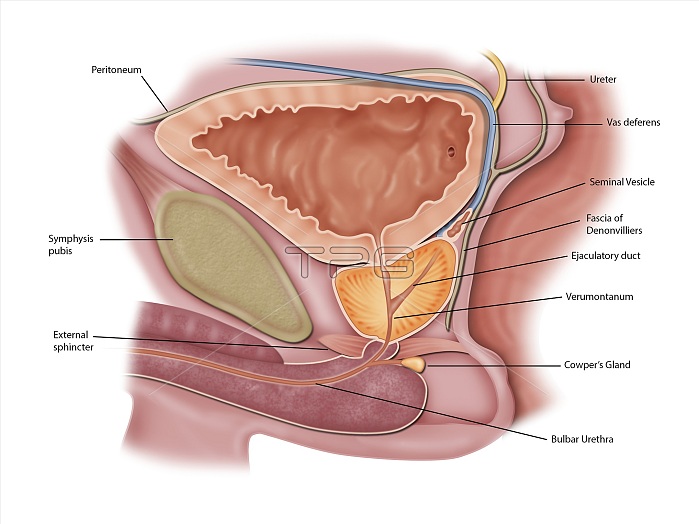
Male urogenital anatomy, illustration. Sagittal sectioned view of aspects of the male reproductive system and urinary system, with the front of the body at left. Urine produced by the kidneys is transported to the bladder (upper centre) via the ureters, followed by urination through the urethra. The longest part of the urethra is the spongy urethra (bulbar urethra). The urethra is also the passage used for reproductive fluids. Sperm arrive from the testicles via the vas deferens, with fluids added from the seminal vesicles, the prostate gland (below bladder) and the bulbourethral gland (Cowper's gland). Within the prostate gland, the ejaculatory ducts and prostatic ducts merge at the verumontanum (seminal colliculus). Passage of fluids into the urethra is controlled by sphincter muscles. Three other structures are labelled here, the pubic bone (symphysis pubis), the membrane enclosing the peritoneal cavity (the peritoneum), and the rectoprostatic fascia (Denonvilliers' fascia) that separates the prostate and bladder from the rectum.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP24703599
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading