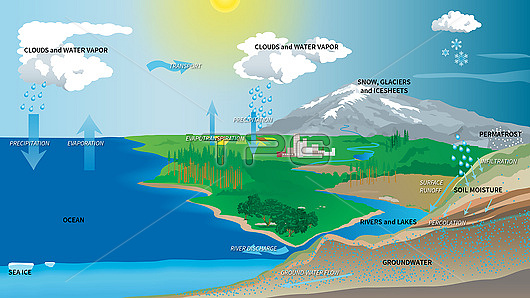
Earth's water cycle, illustration. About 75 percent of the energy (or heat) in the atmosphere is transferred through the evaporation of water, which has a cooling effect on the surface and the lower atmosphere. The Earth's total water supply is estimated to be over 1.3 billion cubic kilometres. The arrows (blue) show some of the ways by which this water is redistributed. This includes evaporation from oceans and land (sea ice also shown) to form clouds from which rain and other forms of precipitation fall. The water then forms rivers and streams and permafrost on land, as well as snow, ice and glaciers in the mountains. Rain infiltrates soil and provides moisture, with percolation through underground rock layers into water tables as groundwater (lower right). Water flows to the sea via surface runoff into rivers and lakes, with river discharge into the oceans. Plants take up water from the soil and release it into the air by transpiration and evaporation (evapotranspiration).
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP25529449
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading