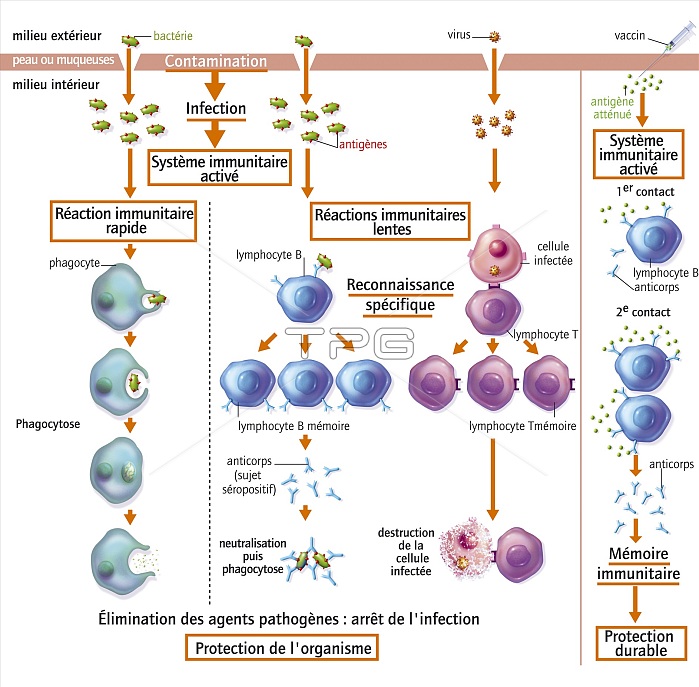
Immune reactions after contamination by bacteria and viruses. Most of this illustration, from left to right, shows the different immune reactions of our body after contamination, either by a bacterium or by a virus. The right-hand column explains the immune reaction triggered after vaccination. After contamination with a pathogen and infection of the body, the immune system activates differently over time. The rapid immune response usually stops the infection. The phagocytes encounter the pathogen and the phagocyte absorbs it to destroy it. If the infection persists, slower immune responses involve specific antigen lymphocytes (in red). B lymphocytes produce antibodies that neutralize antigens. Lymphocytes destroy virus-infected cells by contact. These immune reactions eliminate pathogens and stop infection. Some lymphocytes keep in mind a first contact with an antigen. This immune memory makes the immune response more effective in a second contact with the antigen. Vaccination enables the body to acquire a lasting immune memory.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP25710050
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading