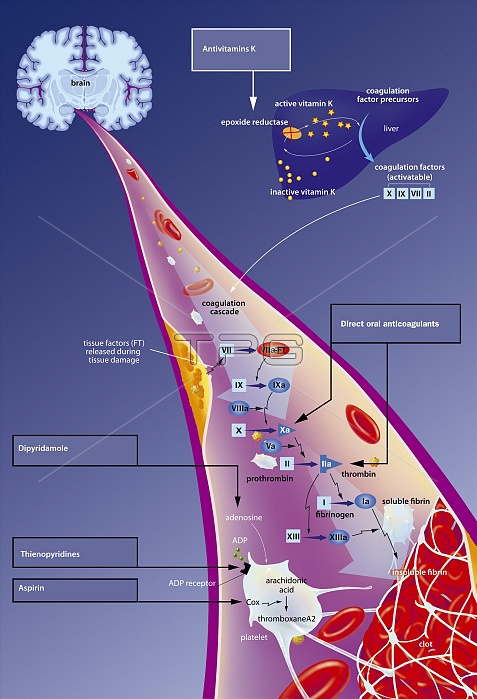
Stroke and antitrhrombics. Top left, the brain in frontal section with its vascularization. A zoom of a sectional vessel departs from the brain to detail the coagulation cascade in the formation of a clot or thrombus (bottom right). In the liver (top right) Inactive vitamin K (yellow beads) becomes active (yellow stars) thanks to epoxide reductase. The active vitamin K will activate the coagulation factors which will in turn cause the coagulation cascade in the blood vessel. In yellow on the left wall of the vessel, an atheroma plaque will release the tissue factor (VII). Below, to the left of the clot, a plaque (white) in the aggregation phase.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP25710094
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading