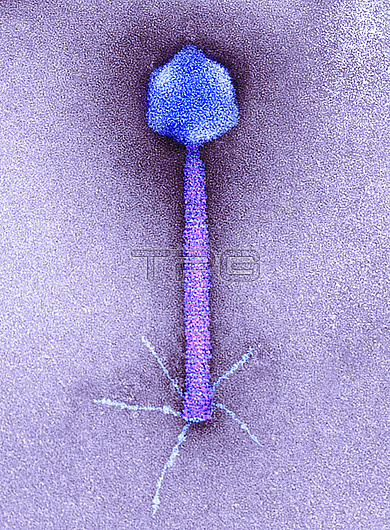
Transmission electron micrograph (TEM) of a P1 bacteriophage. A bacteriophage, or phage, is a virus that infects bacteria, in this case Escherichia coli and Shigella species. It consists of an icosahedral (20-sided) head (top), which contains the genetic material, a tail (cylinder) and tail fibres (leg-like), which fix it to a specific receptor site. On infecting a cell, the bacteriophage can either enter lysogeny or a lytic cycle. In lysogeny, the genome remains dormant in the cell as an autonomous plasmid (circle of DNA). In the lytic cycle, the bacteriophage replicates itself many times and then bursts the bacterial cell, releasing itself into the environment. Magnification: X228,346 when printed at 10 centimetres wide.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP26527596
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading