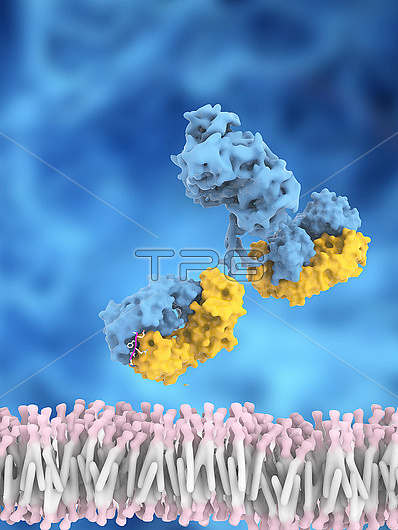
Illustration showing Aducanumab (purple, lower left), a human-derived monoclonal immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody binding to amyloid beta plaques (blue and yellow). Amyloid beta plaques are insoluble aggregates of amyloid beta protein. They are believed to be linked to Alzheimer's disease by causing nerve cell death and affecting nerve cell signalling pathways. Aducanumab binds to amyloid beta plaques by targeting an epitope found on the amyloid beta protein. This causes a reduction in beta amyloid plaques in the brain. Aducanumab could potentially slow down Alzheimer's disease progression, particularly patients in the earlier stages of the disease. On 7th of June 2021, Aducanumab was approved for treatment in Alzheimer's disease by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) through its accelerated approval pathway.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP26557216
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading