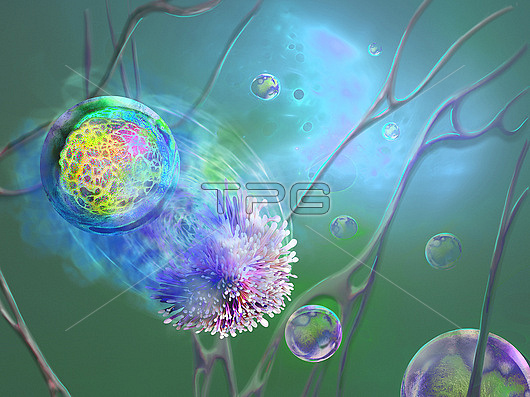
Immune response to inflammation, illustration. A tolerogenic dendritic cell (centre) is seen releasing anti-inflammatory cytokine (signalling molecule) interleukin-10 (IL10, blue). Dendritic cells are immune cells that present pathogens or foreign molecules (antigens) to other cells of the immune system to be eliminated. Tolerogenic dendritic cells (tDCs) are dendritic cells with immuno-suppressive properties that produce a tolerance against antigens so cells do not attack the body's own cells and tissue. One way it can produce tolerance is by inducing normal T-cells (lower left) into regulatory T-cells (Treg) by releasing cytokine IL-10. T lymphocytes, or T cells, are a type of white blood cell and a component of the body's immune system. They recognise a specific site on the surface of a pathogen or foreign object (antigen), bind to it and attract antibodies or cells to eliminate it. Regulatory T cells can suppress responses by T cells to maintain homeostasis in the immune system.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP26624649
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading