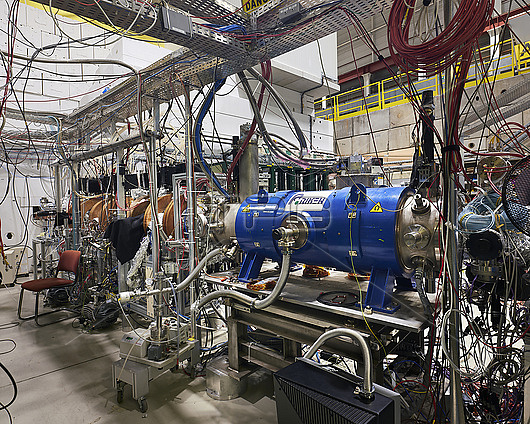
GBAR (Gravitational Behaviour of Antihydrogen at Rest) experiment facility at CERN (European Particle Physics Laboratory). This experiment aims to measure the freefall acceleration of antimatter under gravity. To achieve this, the GBAR experiment starts by combining antiprotons with two antielectrons to create antihydrogen ions with a positive charge. These ions are then brought to microkelvin (approx. -273 degrees Celsius) temperatures using laser-cooling techniques before being stripped of the additional antielectron, transforming them into antihydrogen atoms. The antihydrogen atoms are then allowed to fall from a height of 20 centimetres, and their annihilation at the end of the fall is recorded. By measuring the acceleration of antihydrogen under gravity and comparing it with the acceleration of regular hydrogen, GBAR scientists can detect differences in the behaviour of matter and antimatter. They are also testing the equivalence principle proposed by Albert Einstein, which states that gravitational force on a particle is independent of its internal structure and composition.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP29675993
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
Restriction:
Editorial use only. This image may not be used to state or imply endorsement by CERN or CERN employees of any product, activity or service. Not to be used in a military context.

 Loading
Loading