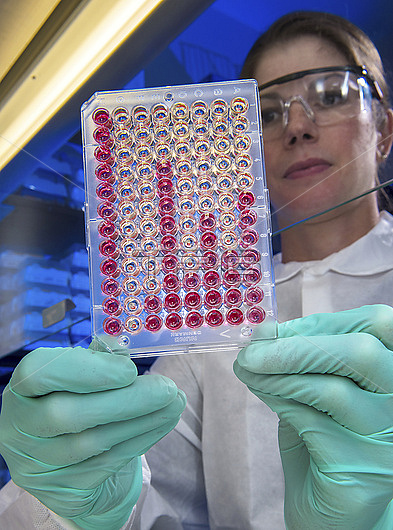
Scientist examining a microtiter plate showing the results of a haemagglutinin inhibition (HI) test, which is used to characterise proteins known as antigens which are found on the surface of viruses. Haemagglutinin (HA) is an antigen found on the surface of influenza (family Orthomyxoviridae) viruses. HA can bind red blood cells in a process called haemagglutination, causing them to form lattices, shown by wells which have gone fully red. HI tests work by adding antibodies (type of protein) which bind to HA, inhibiting the process of haemagglutination. Small red dots indicate where this inhibition has occurred. If one type of antibody inhibits HA in several strains of influenza (indicated by multiple small red dots), it suggests these strains of influenza have similar antigens.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP29814713
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
no
Property Release:
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
Restriction:
Editorial use only

 Loading
Loading