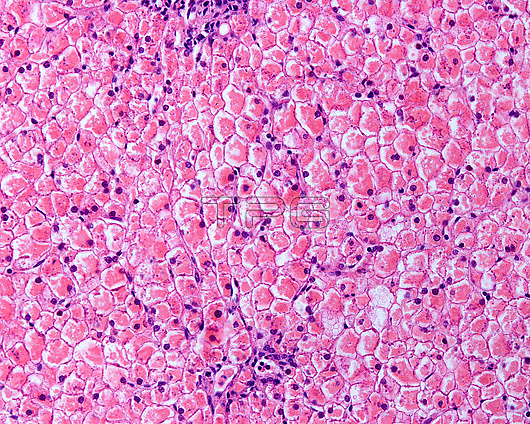
Light micrograph of glycogenosis in a human liver. Hepatic glycogenosis is characterised by excessive glycogen accumulation in hepatocytes (liver cells) and represents a hepatic complication of diabetes that is more likely to occur in patients with longstanding poorly controlled type 1 diabetes. It can also be due to glycogen storage disease type I (GSD I), an inherited disease that results in the liver being unable to properly break down stored glycogen. After conventional tissue preparation (fixation by formaldehyde and staining with haematoxylin and eosin) the glycogen is usually removed from the hepatocytes. Using an alcoholic fixative, the glycogen is preserved, appearing as a pink material that fills the hepatocytes. The accentuated cell membranes and displacement of the nuclei to the cell periphery can still be seen.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP27858495
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading